Welcome to the realm of innovative surveillance where safety and productivity harmoniously coexist. Our multi-faceted video security solutions are designed not just for safeguarding your premises but also to drive operational efficiency and create accountability, all while reducing financial burden and liability risks.

LPR cameras automate gate access for authorized vehicles, streamlining entry while providing real-time security alerts.

Smart alerts can trigger actions like messages, relays, or strobes based on schedules, motion, plates, or custom events.

Our cameras capture full-color video even at night, ensuring clear and reliable surveillance in all conditions.
While employing security personnel could cost upwards of $45,000-$62,000 annually, our video security solutions are a one-time investment for continuous, round-the-clock surveillance. They offer comprehensive coverage across multiple locations and angles, outperforming the limited vantage point of a human guard.
At the heart of our video security solutions are Closed-Circuit TV (CCTV) systems, which transmit secure signals to designated monitors or storage devices. They comprise various integral components: storage hard drives, network video recorders, cables, wiring, and of course, the security cameras themselves.
When it comes to choosing a camera, consider aspects such as resolution, visibility under diverse lighting conditions, and positioning for an optimal field of view. During installation, the camera-to-subject distance should be appropriate, the subject area should be well-lit and in focus, and potential obstructions or glare should be minimized.
Investing in today’s cutting-edge video security solutions involves three key elements: Connectivity, Recorders, and Cameras. Dive deeper into each component by expanding the categories below, and embark on a journey towards comprehensive, versatile, and innovative surveillance solutions.
As technology progresses, CCTV systems continually evolve, with an increasing array of wireless options becoming available. While wireless systems are suitable for consumer applications, they often encounter difficulties when scaling up and generally have less advanced hardware. Wired cameras remain the superior choice due to their cutting-edge technology, dependability, and longevity. Furthermore, wired security camera systems offer greater efficiency in preventing network corruption and hacking compared to their wireless counterparts. Hardwired cameras typically feature technology that is 3 to 5 years more advanced than their consumer-grade wireless equivalents.
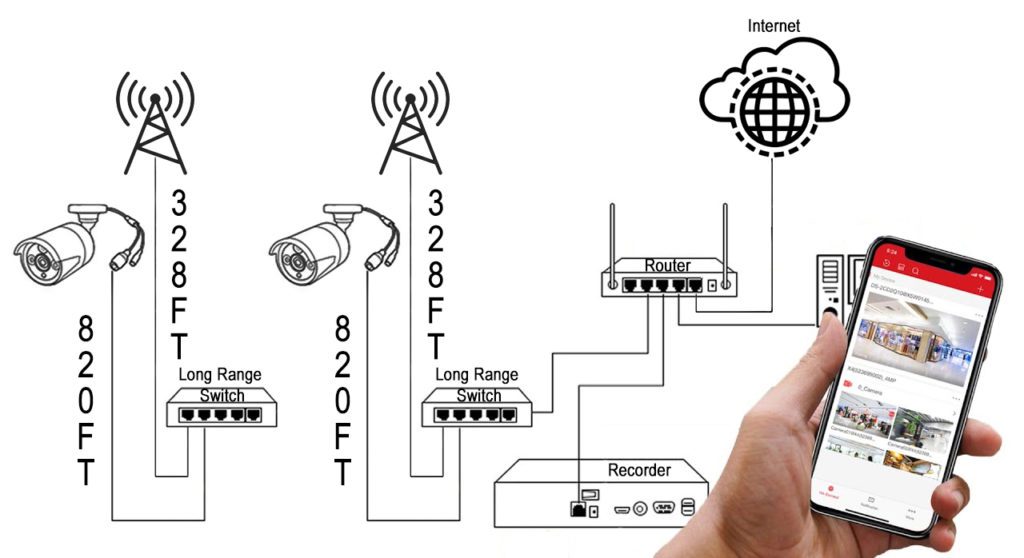
For scenarios where running wires is impractical, hardwired cameras can be converted to wireless using specialized wireless network bridges. These bridges are explicitly engineered to securely and reliably transmit video data from one or even hundreds of IP-based hardwired cameras. However, remote locations that require wireless equipment must have access to power, even if they are several miles away from the recorder.
Cat5E or Cat6 cables are the most prevalent types used in video surveillance, supplying both power and video transmission for the cameras. To shield against corrosion, water, heat, and other factors that could cause damage over time, it’s crucial to implement preventive measures. Some methods to protect your cables include using cable sheaths, conduits, or raceways, installing wiring inside or behind walls, baseboards, and ceilings, or utilizing direct burial outdoor-rated data cables.
Video security solutions have experienced significant advancements, resulting in three primary recording options: Video Management Software (VMS), Network Video Recorders (NVRs), and Digital Video Recorders (DVRs). To make an informed decision on the most suitable choice for your specific needs, it’s essential to understand the unique advantages and disadvantages of each system.
Video Management Software (VMS)
VMS is a versatile video management tool installed on a computer, offering robust functionality and scalability, similar to NVRs. VMS can work seamlessly with equipment from multiple manufacturers, providing flexibility and adaptability in various security setups. A sophisticated VMS typically features enterprise-level capabilities, such as video walls, fail-over, and mapping support.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Network Video Recorders (NVRs)
NVRs are engineered to record and display IP video camera streams on a self-contained recording appliance, offering similar functionality as VMS systems. NVRs connect IP cameras and allow video streams to be sent across a TCP/IP network for storage, recording, and local or remote display via computer workstations or smartphones. NVRs support high-resolution imaging and advanced analytics.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Digital Video Recorders (DVRs)
DVRs record video from coax or RG6 connected cameras, converting the analog or digital signal and encoding the data onto a surveillance-grade hard disk drive. Cutting-edge technologies enable analog cameras to perform digitization and communicate with the DVR as a digital camera using standardized digital over coax protocols, such as CVBS, AHD, CVI, and TVI. However, DVR systems have limitations in camera resolution, typically capped at 4K.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Choosing the right security cameras for your business is crucial, as each type offers unique strengths and weaknesses. Assessing your specific needs and understanding various camera types and technologies will ensure you choose the best fit for your requirements.
Monitoring all entrances and exits is essential, as these points are commonly targeted by criminals. To protect your business interests, consider surveilling areas containing proprietary or valuable materials and files. Proactively securing your business against theft or unauthorized access can yield significant benefits in the long run.
Popular Video Security Solutions for Commercial Use:
Six popular security cameras for commercial purposes are bullet cameras, dome cameras, turret cameras, fisheye cameras, multi-sensor cameras, and PTZ (Pan+Tilt+Zoom) cameras.
Numerous camera types are available, but for our purposes, we will discuss the six most commonly used security cameras for commercial use. The six cameras we will discuss are bullet cameras, dome cameras, turret cameras, fisheye cameras, multi-sensor cameras, and PTZ (Pan+Tilt+Zoom) cameras.
Pros:
Cons:

Pros:
Cons:

Pros:
Cons:

Pros:
Cons:

Pros:
Cons:

Pros:
Cons:

Pros:
Cons:

Pros:
Cons:
Each camera type features specialized technologies that enable it to capture image details that might otherwise be missed. Some of these technologies are universal, standard equipment on all commercial-grade cameras. The list is extensive; some cameras can differentiate between humans and cars, count visitors, perform heat mapping to illustrate heavily trafficked areas at a glance, and alert you when an object appears or leaves the camera’s field of view, among many other features. For brevity, we will detail four of the more commonly used technologies.